Optimizing compiler Scalar optimizations
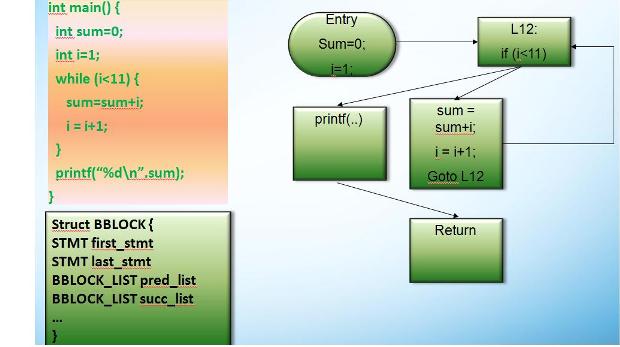
Control Flow Graph
A Control Flow Graph (CFG) represents all paths through a program control could travers during its execution. In a control flow graph each node represents a basic block (a straight-line piece of code without any jumps or jump targets). Jump target starts a block, and jump ends a block. Directed edges are used to represent jumps of the control. There are two specially designated blocks: the entry block, through which control enters into the flow graph, and the exit block, through which all control flow leaves.
The CFG is essential to many compiler optimizations.
Scalar optimizations
There are well-known scalar optimizations such as constant folding, constant propagation and copy propagation.
Constant folding is a process of calculating a constants at compile time.
Constant propagation is substitution of variables with known constant values by these values in the expression.
Copy propagation is substitution of variables by their values.
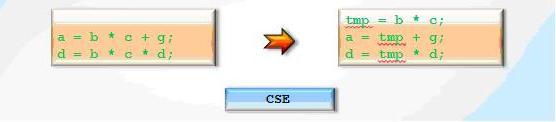
Common subexpressions elimination
Search for identical subexpressions and saving the calculation result in a temporary variable for later reuse.
Dead code elimination
Removal of code that does not change the output of the program.
There are many cases when dead code can appear. It can be the result of scalar optimizations, inlining, etc.