| Китай, ?? |
Optimizing compiler. Loop optimizations
The presentation can be downloaded here.
Loops
In most of the cases, the loops are "hot spots" of the program.
That's why microprocessor architects and compiler developers pay high attention to the loops.
For example, Loop Stream Detector eliminates the sampling and decoding of instructions for the small loops. This is the hardware solution for improving loop performance.
In a compiler, there are many optimizations provided specially for the loop processing.
Loop recognition and classification.
Loop optimizations usually can be performed only for loops with a certain number of iterations and sequentially changing iteration variables. There should no be transitions outside of the loop and calls to unknown functions.
"Good" loops:
for(i=0;i<U;i++) for(i=0;i<U;i++) {
a[i]=b[i]; a[j]=b[i];
j+=c*i; }
i=0; i=0;
do { do {
a[i]=b[i]; a[i]=b[i];
i++;} while(i<U); if(i++>=n) break;
while(1);
"Bad" loops
for(i=0;i<3*i-n;i++)
a[i]=i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
a[i]=i;
if(i<t) break;}
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
a[i]=i;
if(i==t) goto loop_skip;}
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
a[i]=i;
t=g(i);}
Consider the complexity of the used structures.
Avoid loops with an uncertain number of iterations.
Loop Optimizations
Loop invariant code motion is an optimization, which finds and brings outside of the loop expressions, independent of the loop index variables. Such expressions are constant on each iteration.
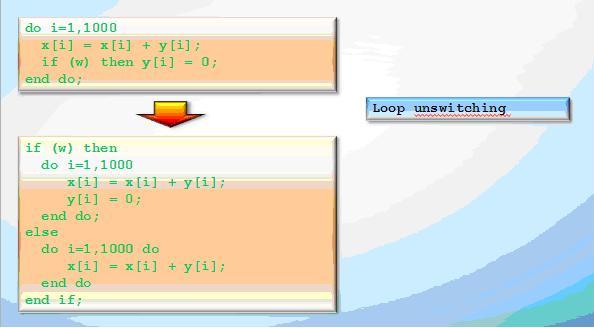
Loop unswitching is an optimization which takes invariant conditional jump out of the loop body by duplicating its code